On March 16, researchers from the International Academic Center of Complex Systems ( IACCS ) of Beijing Normal University at Zhuhai ( BNU Zhuhai ), together with a partner of the Institute of Theoretical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, published their work titled “Neural-network solutions to stochastic reaction networks” in Nature Machine Intelligence, which proposes a general approach to study stochastic reaction networks based on modern machine learning.

Fig: Article published in Nature Machine Intelligence
The stochastic reaction network in which chemical species evolve through a set of reactions is widely used to model stochastic processes in physics, chemistry and biology. To characterize the evolving joint probability distribution in the state space of species counts requires solving a system of ordinary differential equations, the chemical master equation, where the size of the counting state space increases exponentially with the type of species. This makes it challenging to investigate the stochastic reaction network.
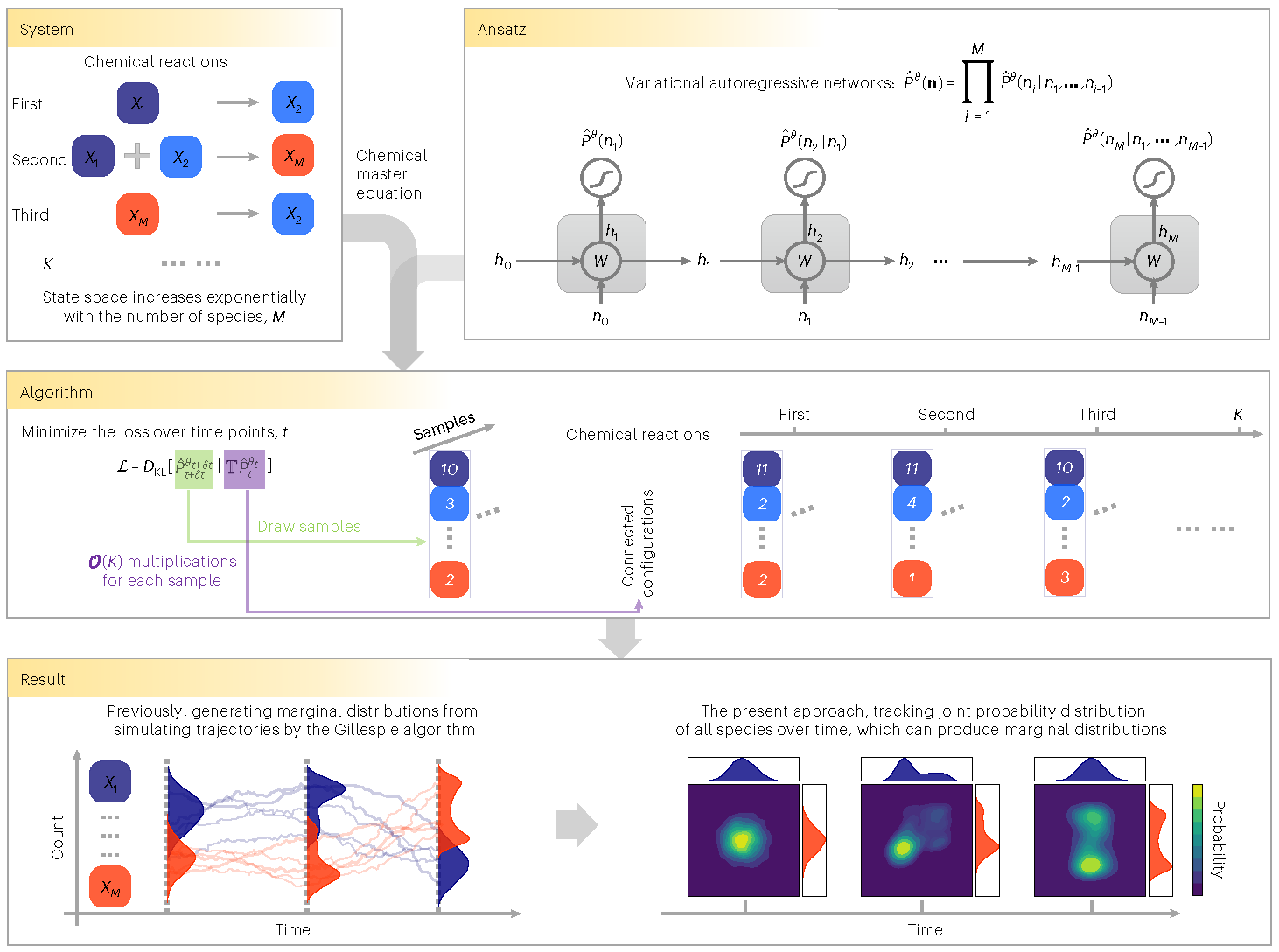
Fig: Tracking the joint probability distribution of stochastic reaction networks over time
The work proposes a machine learning approach using a variational autoregressive network to solve the chemical master equation. Training the autoregressive network employs the policy gradient algorithm in the reinforcement learning framework, which does not require any data simulated previously by another method. In contrast with simulating single trajectories, this approach tracks the time evolution of the joint probability distribution, and supports direct sampling of configurations and computing their normalized joint probabilities.
The authors apply the approach to representative examples in physics and biology, and demonstrate that it accurately generates the probability distribution over time.The variational autoregressive network exhibits plasticity in representing the multimodal distribution, cooperates with the conservation law, enables time-dependent reaction rates and is efficient for high-dimensional reaction networks, allowing a flexible upper count limit. The results suggest a general approach to study stochastic reaction networks based on modern machine learning.
Ying Tang, an associate researcher the International Academic Center of Complex Systems (IACCS) of Beijing Normal University at Zhuhai, and Jiayu Weng, an undergraduate majoring in Systems Sciences and Engineering, are co-first authors. Ying Tang and Prof.Pan Zhang from the Institute of Theoretical Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences are corresponding authors. The International Academic Center of Complex Systems (IACCS) of Beijing Normal University is the first unit of the paper, and the research was strongly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.12105014,11747601,11975294). Nature Machine Intelligence focuses on scientific research results that have important influences on the field. Due to its strict evaluation criteria, the average number of papers included every year is only about 80. The journal is an important journal in the field of computer science and artificial intelligence, the impact factor of which is 25.8 in 2022.
Paper link: https://www.nature.com/articles/s42256-023-00632-6
Free read-only version of the paper: https://rdcu.be/c7MVp
Program package: https://github.com/jamestang23/NNCME


